|
|
American Association of Physics Teachers |
|
|
Neil
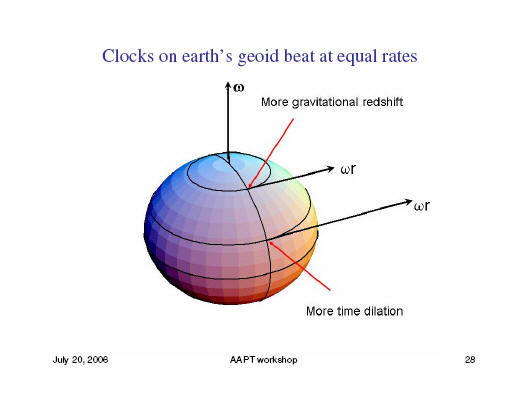
Ashby's TALK
-- p. 6 Relativity in the Global Positioning System from the AAPT Topical Workshop: Teaching General Relativity to Undergraduates Syracuse University, July 20-21, 2006 |
|
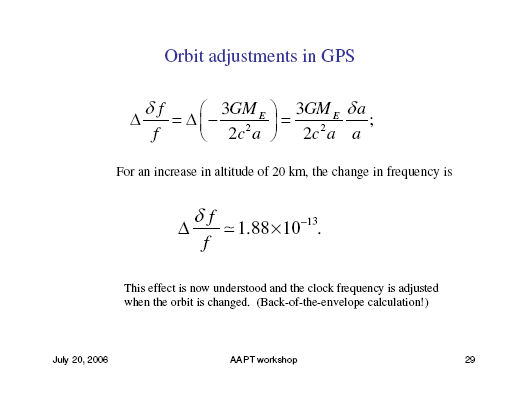
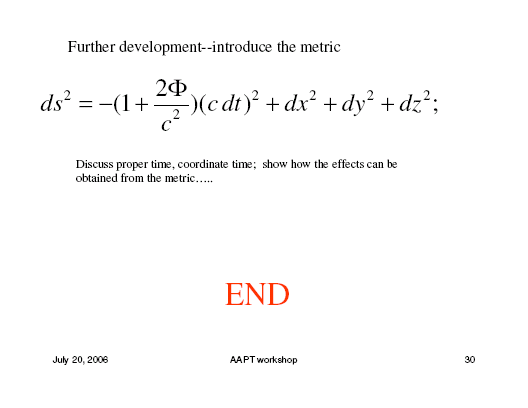
Slides from Ashby's tutorial talk, "Relativity in the Global Positioning System," are given here in six web pages. In the narrative below you can click on any subject to go to its page. Click here for a full PDF version. pg. 1 Ashby showed how the Global Positioning System is an excellent context for teaching relativity. The fundamental principles of relativity are central to a working GPS; an understanding of reference frames, including accelerating frames and the principle of equivalence, is necessary to understand GPS; dealing with the relativity of simultaneity is a central problem of operating a GPS. pg. 2 Ashby shows ways to present to students these basic ideas: pg. 3 Combining the equivalence principle with these ideas Ashby shows that a clock will have its frequency shifted in a gravitational field (gravitational redshift), and, therefore, two identical clocks at different heights will run at different rates. How big will be the difference in rates of a clock on Earth and a clock in orbit? Big enough to cause a navigational error of 13 km in a day if it is not corrected for. pg. 4 Currently, clock frequencies can be stable to parts in 1014 over a week. In one day an error of 10-14 would correspond to an uncertainty of .26 m in position. With such precise timing GPS can use the constancy of c and the accurately known positions of orbiting satellites to determine the distance |r-rj| of the GPS receiver from the jth satellite. Four independent measurements suffice to locate the receiver on the surface of Earth to within a meter. pg. 5 An orbiting clock shows the effects of both the time dilation predicted by special relativity, and the gravitational redshift predicted by general relativity. These tend to cancel. Time dilation in the GPS is negative, arising because the orbiting the satellite is moving relative to the receiver on the ground. The effect of gravitational red shift is positive because the satellite sits in a weaker gravitational field than the receiver. pg. 6 On Earth's geoid the two effects cancel. A clock at the pole runs faster than at the equator because the velocity of the surface is less at the pole. But because Earth is oblate, a clock at the pole is closer to Earth's center than at the equator and so sits in a stronger gravity field and runs more slowly by just the amount to offset time dilation. For a clock in an orbiting satellite the two effects only partially cancel. A change in orbit changes the rate at which the satellite clock runs. A change of 20 km changes the frequency by 1.88 parts in 1013. Whenever a satellite's orbit is changed, the clock rate is corrected accordingly. GPS illustrates many principles of GR and special relativity without new mathematics. To explore further, however, you will need to introduce the metric. |

.jpg)