15
Physics and 21st Century Science Standards: The Role of Physics in the NGSS
Physics is not explicitly differentiated from
chemistry within physical science topics
or DCIs. As a result, there is some overlap.
Schools and teachers are expected to use
their professional discretion to determine
who teaches these concepts and in what
order, although Achieve has released a set
of suggested course maps for middle and
high school. In some cases, fundamental
physics concepts are not mentioned at
all, and teachers are expected to use good
judgment when making decisions about
detailed curriculum, using the NGSS only
as guideposts for student achievement
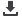
along the way. Table 3 shows high school
physics-related NGSS, organized by topic.
TOPIC
KEY PHYSICS
Structure and Properties of Matter
Table 3: High school physics-related standards
HS-PS1-3: Plan and conduct an investigation to gather evidence to compare the
structure of substances at the bulk scale to infer the strength of electrical forces
between particles.
HS-PS1-8: Develop models to illustrate the changes in the composition of the
nucleus of the atom and the energy released during the processes of fission, fusion,
and radioactive decay.
HS-PS2-6: Communicate scientific and technical information about why the
molecular-level structure is important in the functioning of designed materials.
***ENGINEERING DESIGN***
Coulomb’s Law
Nuclear Physics
Materials Science
HS-PS2-1: Analyze data to support the claim that Newton’s second law of motion
describes the mathematical relationship among the net force on a macroscopic
object, its mass, and its acceleration.
HS-PS2-2: Use mathematical representations to support the claim that the total
momentum of a system of objects is conserved when there is no net force on the
system.
HS-PS2-3: Apply scientific and engineering ideas to design, evaluate, and refine
a device that minimizes the force on a macroscopic object during a collision.
***ENGINEERING DESIGN***
HS-PS2-4: Use mathematical representations of Newton’s Law of Gravitation and
Coulomb’s Law to describe and predict the gravitational and electrostatic forces
between objects.
HS-PS2-5: Plan and conduct an investigation to provide evidence that an electric
current can produce a magnetic field and that a changing magnetic field can
produce an electric current.
Newton’s Laws
Kinematics
Impulse = ΔMomentum
Conservation of Energy
Uni. Gravitation
Coulomb’s Law
Current
Magnetism
Induction
Forces and Interactions
Physics in
the NGSS